Blockchain and NFTs Explained
Still don’t understand exactly what blockchain technology is? Check out our quick-start guide to make sense of blockchain and explore its practical applications like HKUST blockcerts and NFTs.
Introduction
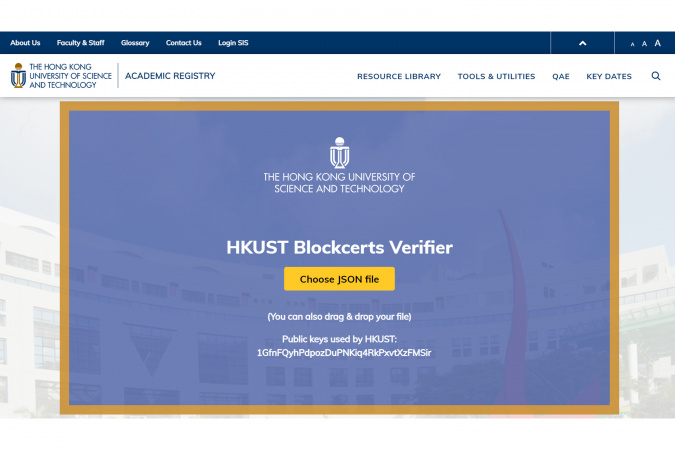
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) is the first university in Hong Kong to issue official documents in a secure electronic format which are verifiable. Blockcerts program utilizes the blockchain technology that registers and verifies the issued electronic documents. By registering on the blockcerts server, the documents are cryptographically signed, tamper-proof, and shareable. Besides blockcerts, you may have heard about Bitcoin on the news and social media, but the blockchain technology that powers Bitcoin is mysterious to the general public. What is a blockchain and what are its practical applications? What are the benefits of the blockchain-based applications?
What is a blockchain?
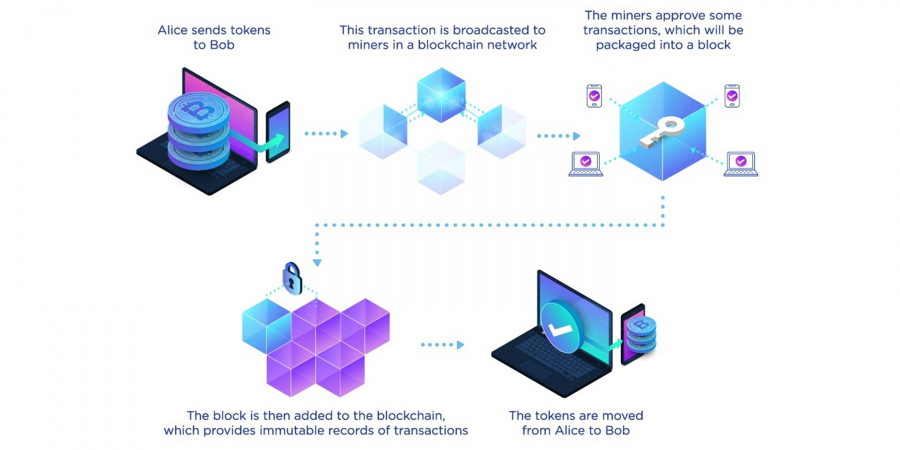
A blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in maintaining secure and decentralized transaction records for cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin. The cutting-edge innovation of blockchains guarantees the fidelity and security of data records and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party. Those who run blockchain programs, known as the miners, are responsible for maintaining the security of a blockchain with consensus protocols such as proof of work (more computations lead to more rewards). Such decentralization makes the key to blockchain security because no single one can control the system or modify the data recorded on the blockchain (unless under the 51% attack, which is unlikely or nearly impossible for popular blockchains), that is the reason why blockchains are widely regarded as secure.
Benefits of blockchain-based applications
Due to the immutability of a blockchain, we can store data on a public blockchain such as Bitcoin, and the stored data is likely to be publicly available forever. This is fundamentally different from storing data on a cloud server offered by a company because data loss can happen due to many potential reasons: the company changes its data storage policy or even shuts down the cloud service. Therefore, people trust that their data or transactions can be stored eternally on a public blockchain. With the trust from the general public, many blockchain applications have come into reality today, such as the decentralized finance (DeFi) and decentralized computing platforms (i.e. Ethereum). Here, we introduce two practical blockchain applications: Blockcerts and Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs).
Application of blockchains
With the immutability property of a blockchain, a direct practical application is document/certificate verification by posting (the hash of) documents on the blockchain by an authority such as a university or an institute. HKUST is a pioneer in utilizing the blockchain-based Blockcerts to issue official documents in a secure and verifiable electronic format, where the functional system at HKUST was developed by its students and staff. In short, Blockcerts is a platform for issuing, viewing, and verifying blockchain-based documents (currently based on Bitcoin). With such a blockchain technology, students can receive digital documents and certificates that can be easily verified on a blockchain because the hash of these documents is recorded in a block on the Bitcoin blockchain by HKUST. A third party including potential employers can directly and instantly verify the authenticity of these documents on the blockchain without the need to contact HKUST to further verify the documents, which is often time-consuming. This also prevents the fabrication of fake digital certificates because these fake certificates will not be verified on the blockchain.
Another interesting application of blockchains is the non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which attract numerous users and investors. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum which can be traded or exchanged for one another, each NFT has a unique digital identifier that makes it impossible for NFTs to be exchanged for or equal to one another, meaning they are not mutually interchangeable, hence not fungible. A non-fungible token can represent the ownership of a digital or physical asset (i.e. digital art or a painting) on a blockchain. A key property of NFTs is that they can be easily traded and sold on a blockchain (mostly on Ethereum now). A representative example is the CryptoKitties where users can buy, own, and sell virtual cats. Singaporean Chinese musician Hanjin Tan, has released NFT new song “Nobody Gets Me” in April 2021. He was the first amongst China’s music scene. In Hong Kong, there is a galley at K11 MUSEA that aiming to provide a safe, fair, and dynamic space for all interested in the rising NFT (non-fungible token) market, whereas NFT museum opens at Hysan Place in Causeway Bay amid the art trend. Mandycat, a famous Hong Kong illustrator, also creates and sells her artworks in the NFT world.
There are also marketplaces such as OpenSea for users to buy and sell NFTs. These platforms are similar to eBay; users can place bids for a certain NFT, and the highest bidders will win the bid. Currently, there are some hypes about NFTs as the prices of an NFT can be as high as millions of US dollars. The marketplace of NFTs creates a new way for artists to sell their artworks easily through the blockchain.
Example of NFTs applications
On the other hand, we should be cautious about the information of NFTs. The past year saw an international boom in NFTs, but criminal activity has also increased in this sector. It is possible to have “fake” NFT transactions, conducted by the same person or group as both the buyer and seller, to push the price of an NFT. Also, there are scams on the NFTs marketplaces: for instance, a fake Banksy (famous street artist) NFT was sold for more than US$300,000 but Banksy confirmed that he had never created any NFT. It may not be easy to verify whether an NFT is authentic. Price-wise, there is no standard market price for NFTs, so the price of an NFT could plummet in a short period of time.
In summary, we have witnessed booming prices of cryptocurrencies and thousands of applications on blockchains nowadays. Blockchains are changing our daily lives in ways that we might not even notice. It is always a good idea to know the latest trends in technology such as blockchain and understand the technology behind.
By Prof. CHEN Qifeng, Assistant Professor of Computer Science & Engineering and Electronic & Computer Engineering
(This article was originally published on STEM@HKUST here.)